THE 5 GREEN BEANS PLANT STAGES – THEIR MESMERIZING BEAUTY, CARE AND MAINTENANCE
GREEN BEANS PLANT STAGES -Green beans are young and unripe fruits of the cultivars of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris), belonging to the family Leguminosae or Fabaceae. These fruits have a plethora of common names, such as string beans, French beans, and snap beans, this is primarily because it is called with a different name in each different place. For example, it is called ‘Baguio beans’ in the Philippines to distinguish it from the yard-long beans. It also has a lot of health benefits; The important distinguishing factor about green beans is that these crops are harvested and consumed fully along with the pod before the seeds have fully matured.
FACTORS REQUIRED FOR THE GROWTH OF GREEN BEANS
The requirements of the plant have to be understood to cultivate the plant successfully. This fetches a high market price for the produce and ensures a continuous supply of garden beans all year round in your garden.
| FACTOR | REQUIREMENT |
| Soil | Green beans thrive in well-drained soil with good fertility. Sandy loam or loamy soils are ideal for their growth.The ideal pH range is 6.0-7.2 (slightly acidic to neutral)Organic matter should be added to the soil to improve its water retention capacity and fertility status. |
| Light | Green beans require a minimum of 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day for optimal growth. Insufficient sunlight may result in weak, leggy plants with reduced fruitingWhile green beans thrive in full sun, they can tolerate some degree of partial shade. However, too much shade can hinder their growth and yield |
| Temperature | Green beans are warm-season crops that prefer temperatures between 70°F and 85°F (21°C-29°C) for optimal growth. Cooler temperatures below 60°F (15°C) can slow down growth.Green bean plants are sensitive to frost. Hence, they should be planted after the danger of frost has passed and soil temperature has warmed up. |
| Climate | Green beans grow well in regions with a moderate climate, although they can be grown in both cooler and hotter climates if proper care is taken. |
| Water | Green beans require consistent soil moisture to thrive. Watering deeply and regularly, ensuring the soil is evenly moist but not waterlogged, is vital.Green beans require consistent soil moisture to thrive. Watering deeply and regularly, ensuring the soil is evenly moist but not waterlogged, is vital. |
| Nutrient Requirement | Green bean plants require a sufficient supply of nitrogen for healthy leaf growth and overall vigour. Organic matter and nitrogen-rich fertilizers can help meet this need.Adequate phosphorus and potassium levels are necessary for robust root development, flowering, and fruit set in green beans. Balanced fertilizers or compost can provide these nutrients. |
GROWTH STAGES OF GREEN BEANS
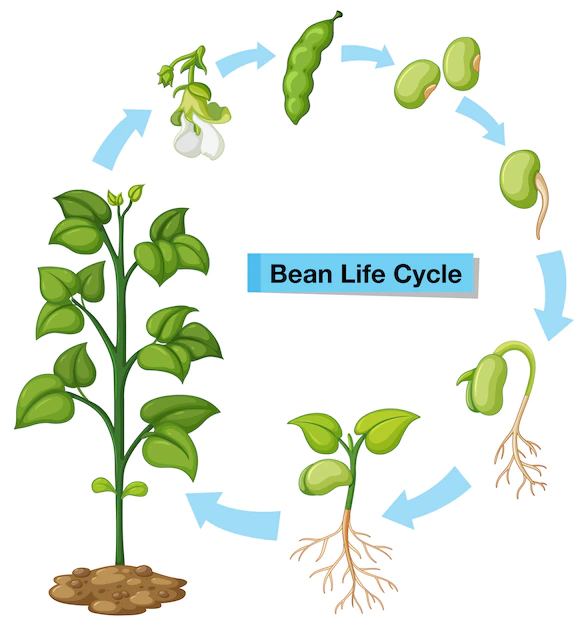
STAGE 1: GERMINATION STAGE OF GREEN BEANS:
From seed to plant transformation, the germination stage is an essential stage of growth as it forms the foundation for healthy plants which are vigorous and high yielding.
Pre-planting requirements:
- Good quality seeds have to be selected, which are certified as organic and free from any damage or disease.
- Pre-sprouting and pre-soaking of seeds can be considered as these processes give a head start in the germination process and ensure uniform planting.
- Pre-sprouting can be done by placing the seeds in a damp towel or cloth until they begin to sprout. And soaking softens the seed coat and quickens the rate of germination.
- Soil has to be well-drained and rich in organic matter. To improve drainage, add compost or well-rotted manure to the soil.
Planting conditions requirements:
- Plant the germinated seeds in the prepared soil placing them about 1 inch deep and 3 inches apart.
- Keep the soil well irrigated but there should not be any waterlogging as it causes damage to the growing seedlings.
- Germination takes about 7 – 10 days.
Care and maintenance of germinating seedlings:
- Thinning should be done once the seedlings emerge. The spacing should be around 4 inches between two plants.
- Mulching should be done to help conserve the water the plants need and also to control weed growth.
- Irrigate regularly after checking the moisture level in the soil. Overwatering leads to root rot in seedlings.
- Pest and disease infection has to be controlled by the use of organic pest control methods and proper air circulation for the plants.
STAGE 2: VEGETATIVE STAGE OF GREEN BEANS:
This stage involves the development of the leaf and the stems. In this stage, there’s an increase in the size of the plant. And the main importance of this stage is getting the plant ready for the flowering stage.
Irrigation, sunlight, and nutrient requirement, spacing, and mulching should be done correctly to ensure robust stem and leaf growth. Mulching is done to preserve soil moisture loss by evaporation and to suppress weed growth.
- Pruning and shaping of plants:
Based on plant stature, bean plants can be divided into determinate and indeterminate types. During the vegetative stage, this process is done to improve the plant’s stature. It encourages bushy growth by promoting lateral branching, giving it a bushy appearance. Removing diseased or damaged leaves prevents the spread of the diseases
.
- Pest and disease management:
Pest and disease control is essential for proper growth and development of plants. It can be done by regularly inspecting the plants and then using integrated pest control measures such as introducing beneficial insects such as bees or using organic pesticides such as neem to control pest infestation. For more information visit – DOES NEEM OIL KILL ANTS? – Times of Agriculture
- Staking –
Indeterminate green bean types require support to grow as the plants have a fragile stem system.
- Fertilizer application –
It is advised to conduct a soil test and adjust the fertilizer dose s required. Switching to organic fertilizers is recommended so that a low release of nutrients takes place. Organic fertilizers also ensure that the fertility of the soil is maintained and sustainable use of land.
STAGE 3: FLOWERING STAGE IN GREEN BEANS
It is the previous stage of fruit development. The plants produce small delicate white or purple flowers Proper pollination and air circulation is essential in this stage.

- Pollination and the role of pollinators:
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the male flower to the female flower parts, primarily the ovary. It is a vital process that ensures pod development seed set. Pollinators play a big role in this process even though it’s a self-pollinated crop. Pollinators such as bees and others visit flowers for nectar and they act as a medium of transfer of pollen grains.
- Proper air-circulation;
Providing air circulation is essential as the medium for the dispersal of pollen and for the control of diseases and Mold. Hence, increasing the spacing and proper ventilation in case of protected cultivation ensures a good harvest.
STAGE 4: FRUIT DEVELOPMENT STAGE OF GREEN BEANS
The pollinated flowers undergo fertilization and the pod development takes place here. The pollinated flower forms small pods, which later develop into bigger and elongated pods as the green beans slowly fill up the conditions required for the proper growth of green beans are to be given to ensure a bountiful harvest.


Managing weed competition:
- Mulching-
Apply a top layer of mulch which can be organic or polythene. Examples of organic mulch include wood chips, straw, etc.
Importance-
- Conservation of moisture in the soil
- Temperature regulation
- Improving the soil structure.
- Pre-emergence herbicides-
Pre-emergence herbicides such as pendimethalin are used to prevent the germination of weed seeds in the field. Caution should be taken to ensure no damage to the seeds of green beans is caused due to the herbicides by checking the dosage and requirement of the field.
- Pest and disease management should be done regularly.
STAGE 5: HARVESTING STAGE OF GREEN BEANS
This is the last stage of the development of green beans. Here the beans fully develop, and the harvest is done based on the maturity indices.

Maturity indices of green beans are:
- Pods must be fully plump, firm, and elongated.
- The pods should be crisp, easy to break with no signs of softness or limpness.
- The seeds should be checked inside the pods. The seeds should be well-formed but not too large.
Harvesting techniques
- Hand-picking – A most effective and easy method of harvesting. Snap the beans from the peduncle using fingers or shears ensuring less or no damage to the plants.
- Harvesting frequency – The harvesting of indeterminate varieties should be done once every two to three days.
- Harvest in the morning – Harvesting should be done in the early morning hours. The tender pods remain crisp here.
- Harvest the crops from the bottom of the plant which ensures proper air circulation. This ensures air circulation and sufficient sunlight exposure.
CONCLUSION:
Looking at these growth stages shows us the enchanting changes that take place in the green bean plants from seeds to harvest. Each stage is essential and care and maintenance of the plants during each stage is essential to ensure a bountiful harvest. Green bean cultivation can be exciting and educative for all the gardeners.
Latest Post
- How to take care of Lavender Plants Indoors

- 15 Types of Houseplants With Big Leaves

- Best 20 Types of Fuzzy Succulent Plants

- 15 Types of Ice Plants to Transform Your Garden into a Vibrant Oasis

- Top 20 Types of Begonia Plants to Cheer You up Everyday

- How to Care for Dawn Redwood Bonsai: Convert a Giant into Miniature.

- Top 15 Types of Monstera Plants You Should Know About.

- How to Care for Pearls and Jade Pothos

- How to Grow Cherry Blossom Bonsai From Seed: Improved Methods and Care.

- How to Grow Dragon Fruit from Seed Effectively : Best Method

- 15 Different Types of Holly Bushes to Enhance the Beauty of Your Garden

- Amazing 15 Different Types of Alocasia with pictures


